
Vipin Chandra: L-Leucine in Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation
Vipin Chandra, Director of Matcare Maternity, shared a post on LinkedIn:
“L-Leucine in Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation (COH):
A Metabolic Adjuvant Worth Serious Clinical Attention
Poor ovarian response remains one of the most frustrating challenges in ART. Despite protocol refinement and gonadotropin escalation, outcomes often plateau—especially in women with diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) and hypo-responsive follicles.
Increasingly, attention is shifting upstream—from hormones alone to the intracellular metabolic pathways that govern follicular competence.
One nutrient drawing justified mechanistic interest is L-Leucine.
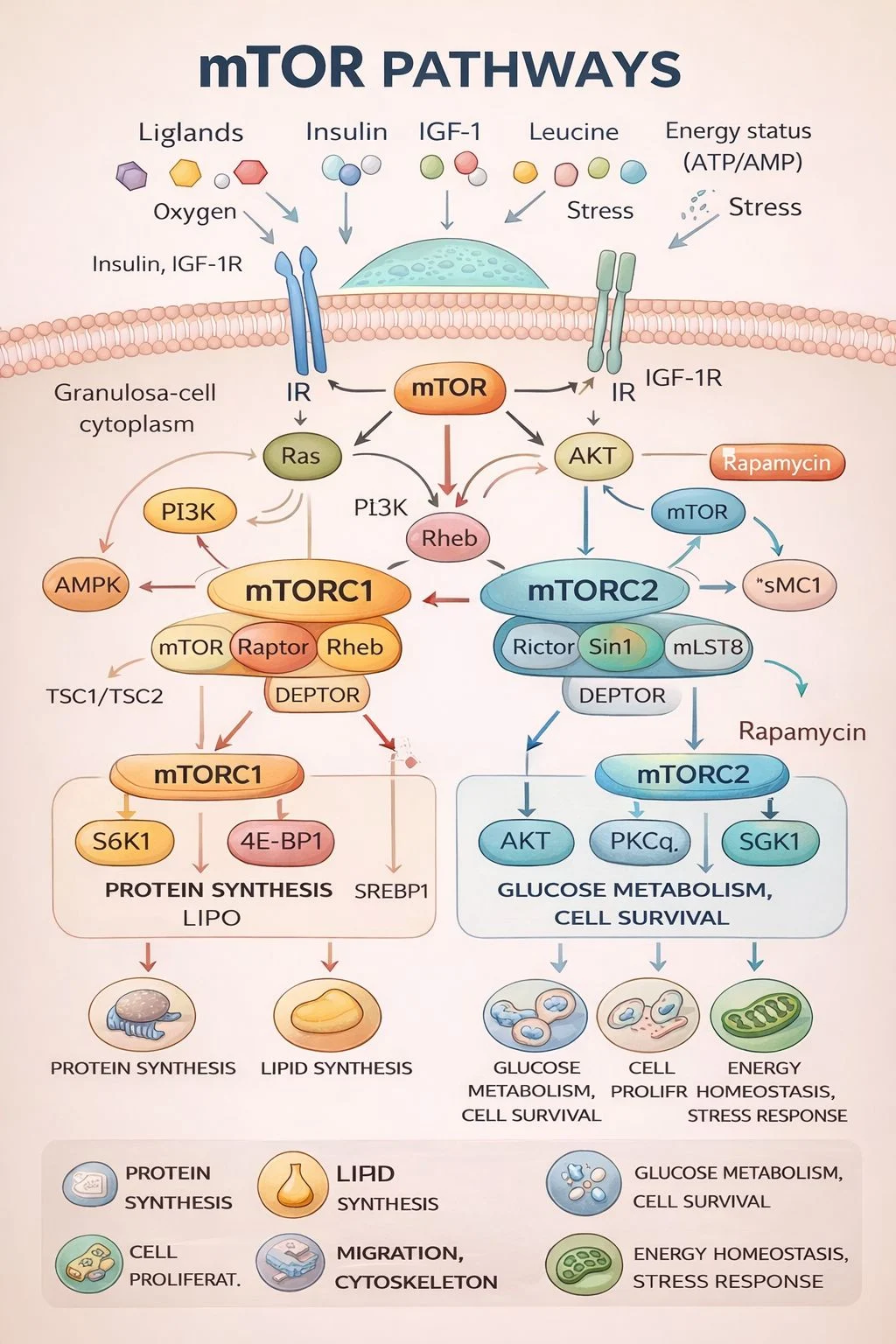
Why L-Leucine Matters Biologically
L-Leucine is a branched-chain amino acid and the most potent physiological activator of the mTOR pathway, a central regulator of:
- granulosa cell proliferation
- protein synthesis
- mitochondrial function
- steroidogenesis
- follicular growth and survival
mTOR signaling is now well established as essential for follicular activation and oocyte competence.
Adhikari et al., PNAS 2010
Mechanistic Advantage in Low-Reserve Ovaries
Unlike insulin-dependent activators, L-Leucine directly activates mTORC1 via Rag-GTPase signaling, supporting cellular metabolism even under stress conditions—precisely the environment seen in aging or hypo-responsive ovaries.
Wolfson et al., Science 2016
Granulosa cells are highly amino-acid sensitive, and preclinical work shows leucine improves:
- mitochondrial activity
- steroidogenic capacity
- granulosa cell survival
Zhang et al., Biology of Reproduction 2017
What Clinical Data Suggest So Far
While IVF-specific RCTs isolating L-Leucine are limited, human nutritional and metabolic studies consistently suggest that optimizing amino-acid–mTOR signaling improves ovarian responsiveness.
L-Leucine has also been studied as part of multi-nutrient metabolic strategies, commonly combined with:
- myo-inositol (FSH/insulin signaling, oxidative stress reduction)
- selenium (steroidogenesis, antioxidant support)
Genazzani et al., Gynecological Endocrinology 2018
Palomba et al., Human Reproduction Update 2021
Clinical Interpretation (Balanced, Not Hype)
At present, L-Leucine should be viewed as a metabolic adjuvant—not a standalone solution.
Its potential role appears strongest in:
- DOR / POSEIDON low-prognosis patients
- hypo-responsive granulosa cell environments
- aging ovaries with metabolic stress
When combined thoughtfully with agents like myo-inositol and selenium, L-Leucine may offer dual-pathway support:
mTOR activation + insulin/FSH signaling optimization
What is urgently needed:
- well-designed RCTs isolating L-Leucine
- follicular-fluid and granulosa-cell human studies
- POSEIDON-stratified outcome analysis.”
Stay updated on all scientific advances in the field of fertility with Fertility News.
-
Oct 11, 2025, 06:44The Global IVF Market Is Set to Reach $65B by 2032 – Meddilink
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:59Unlocking the Potential of Menstrual Blood in Health Testing – Global Women’s Health Innovation Conclave
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:57New Insights on Oocyte Yield in Endometriosis and PCOM – RBMO
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:51Transform Your Expertise with ESHRE eCampus Learning – ESHRE
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:46Accelerate Your Growth at the AP3G National Meeting – ASRM
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:43Debojit Saha: Unraveling Chromosomal Errors in Aging Human Eggs
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:38Silvia Vannuccini: RBMO Highlights Key Insights on Adenomyosis Awareness
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:32Maximilian Attwood: Challenging Medical Misogyny in Endometriosis Research
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:29Ioakeim Sapantzoglou: New Perspectives on Fetal Growth Restriction and Genetic Testing
-
Jan 28, 2026, 16:26Enhancing Pre-Eclampsia Prediction with Doppler Indices – ISUOG
